Fractionating Column on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A fractionating column or fractional column is an essential item used in the
A fractionating column or fractional column is an essential item used in the
 A laboratory fractionating column is a piece of glassware used to separate vaporized mixtures of liquid compounds with close volatility. Most commonly used is either a
A laboratory fractionating column is a piece of glassware used to separate vaporized mixtures of liquid compounds with close volatility. Most commonly used is either a
 In industrial uses, sometimes a packing material is used in the column instead of trays, especially when low pressure drops across the column are required, as when operating under
In industrial uses, sometimes a packing material is used in the column instead of trays, especially when low pressure drops across the column are required, as when operating under
Use of distillation columns in Oil & GasDistillation Theory
by Ivar J. Halvorsen and Sigurd Skogestad, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
by Ming Tham, Newcastle University, UK
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140713020048/http://www.distillationgroup.com/distill.htm , date=2014-07-13 by the Distillation Group, USA
Distillation simulation softwareFractional Distillation Explained for High School Students
Distillation Chemical equipment Fractionation fr:Distillation fractionnée it:Colonna di distillazione
 A fractionating column or fractional column is an essential item used in the
A fractionating column or fractional column is an essential item used in the distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separation process, separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distilla ...
of liquid mixtures to separate the mixture into its component parts, or fractions, based on the differences in volatilities. Fractionating columns are used in small scale laboratory distillations as well as large scale industrial distillations.
Laboratory fractionating columns
 A laboratory fractionating column is a piece of glassware used to separate vaporized mixtures of liquid compounds with close volatility. Most commonly used is either a
A laboratory fractionating column is a piece of glassware used to separate vaporized mixtures of liquid compounds with close volatility. Most commonly used is either a Vigreux column
In chemistry, a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vaporsthat is, turn them into liquidsby cooling them down.
Condensers are routinely used in laboratory operations such as distillation, reflux, and extraction. In distillat ...
or a straight column packed with glass beads or metal pieces such as Raschig ring
Raschig rings are pieces of tube, approximately equal in length and diameter, used in large numbers as a packed bed within columns for distillations and other chemical engineering processes. They are usually ceramic, metal or glass and provide a la ...
s. Fractionating columns help to separate the mixture by allowing the mixed vapors to cool, condense
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to ...
, and vaporize again in accordance with Raoult's law. With each condensation-vaporization cycle, the vapors are enriched in a certain component. A larger surface area allows more cycles, improving separation. This is the rationale for a Vigreux column or a packed fractionating column. Spinning band distillation
Spinning band distillation is a technique used to separate liquid mixtures which are similar in boiling points. When liquids with similar boiling points are distilled, the vapors are mixtures, and not pure compounds. Fractionating columns help sepa ...
achieves the same outcome by using a rotating band within the column to force the rising vapors and descending condensate into close contact, achieving equilibrium more quickly.
In a typical fractional distillation, a liquid mixture is heated in the distilling flask, and the resulting vapor rises up the fractionating column (see Figure 1). The vapor condenses on glass spurs (known as theoretical trays or theoretical plates) inside the column, and returns to the distilling flask, reflux
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions ...
ing the rising distillate vapor. The hottest tray is at the bottom of the column and the coolest tray is at the top. At steady-state conditions, the vapor and liquid on each tray reach an equilibrium. Only the most volatile of the vapors stays in gas form all the way to the top, where it may then proceed through a condenser, which cools the vapor until it condenses into a liquid distillate. The separation may be enhanced by the addition of more trays (to a practical limitation of heat, flow, etc.).
Industrial fractionating columns
Fractional distillation is one of theunit operations
In chemical engineering and related fields, a unit operation is a basic step in a process. Unit operations involve a physical change or chemical transformation such as separation, crystallization, evaporation, filtration, polymerization, isomeriza ...
of chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials int ...
. Fractionating columns are widely used in chemical process industries where large quantities of liquids have to be distilled. Such industries are petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
processing, petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable so ...
production, natural gas processing, coal tar
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psoriasi ...
processing, brewing, liquefied air
Liquid air is air that has been cooled to very low temperatures ( cryogenic temperatures), so that it has condensed into a pale blue mobile liquid. To thermally insulate it from room temperature, it is stored in specialized containers ( vacuum i ...
separation, and hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ...
solvents production. Fractional distillation finds its widest application in petroleum refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefie ...
. In such refineries, the crude oil feedstock is a complex, multicomponent mixture that must be separated. Yields of pure chemical compounds are generally not expected, however, yields of groups of compounds within a relatively small range of boiling points
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envir ...
, also called ''fractions'', are expected. This process is the origin of the name ''fractional distillation'' or ''fractionation''.
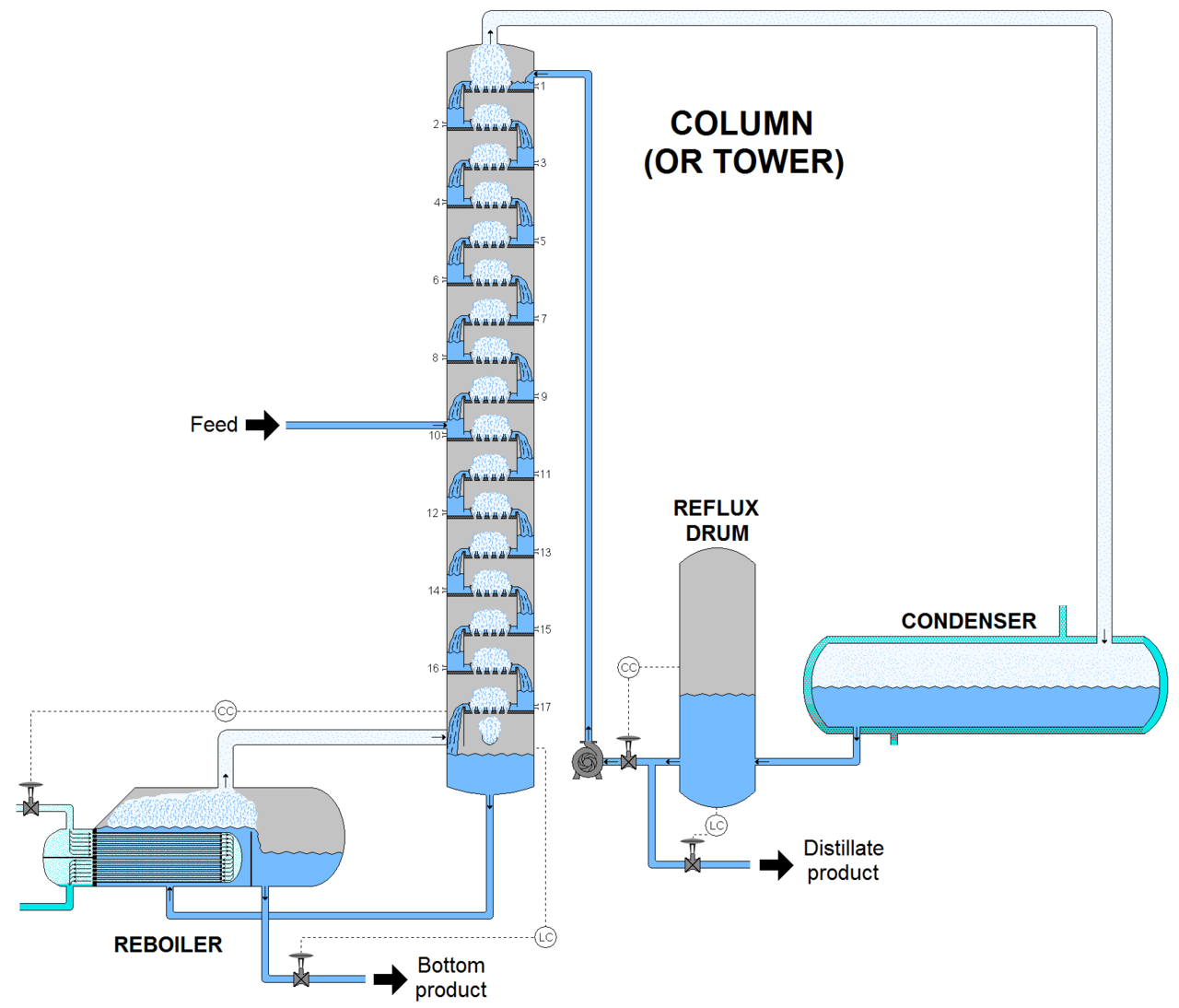
Distillation is one of the most common and energy-intensive separation processes. Effectiveness of separation is dependent upon the height and diameter of the column, the ratio of the column's height to diameter, and the material that comprises the distillation column itself. In a typical chemical plant, it accounts for about 40% of the total energy consumption. Industrial distillation is typically performed in large, vertical cylindrical columns (as shown in Figure 2) known as "distillation towers" or "distillation columns" with diameters ranging from about 65 centimeters to 6 meters and heights ranging from about 6 meters to 60 meters or more.
Industrial distillation towers are usually operated at a continuous steady state. Unless disturbed by changes in feed, heat, ambient temperature, or condensing, the amount of feed being added normally equals the amount of product being removed.
The amount of heat entering the column from the reboiler and with the feed must equal the amount heat removed by the overhead condenser and with the products. The heat entering a distillation column is a crucial operating parameter, addition of excess or insufficient heat to the column can lead to foaming, weeping, entrainment, or flooding.
Figure 3 depicts an industrial fractionating column separating a feed stream into one distillate fraction and one bottoms fraction. However, many industrial fractionating columns have outlets at intervals up the column so that multiple products having different boiling ranges may be withdrawn from a column distilling a multi-component feed stream. The "lightest" products with the lowest boiling points exit from the top of the columns and the "heaviest" products with the highest boiling points exit from the bottom.
Industrial fractionating columns use external reflux to achieve better separation of products. Reflux refers to the portion of the condensed overhead liquid product that returns to the upper part of the fractionating column as shown in Figure 3.
Inside the column, the downflowing reflux liquid provides cooling and condensation of upflowing vapors thereby increasing the efficacy of the distillation tower. The more reflux and/or more trays provided, the better is the tower's separation of lower boiling materials from higher boiling materials.
The design and operation of a fractionating column depends on the composition of the feed as well as the composition of the desired products. Given a simple, binary component feed, analytical methods such as the McCabe–Thiele method
The McCabe–Thiele method is a chemical engineering technique for the analysis of binary distillation. It uses the fact that the composition at each theoretical tray (or equilibrium stage) is completely determined by the mole fraction of one of ...
or the Fenske equation
The Fenske equation in continuous fractional distillation is an equation used for calculating the minimum number of theoretical plates required for the separation of a binary feed stream by a fractionation column that is being operated at total ...
can be used. For a multi-component feed, simulation models are used both for design, operation, and construction.
Bubble-cap "trays" or "plates" are one of the types of physical devices, which are used to provide good contact between the upflowing vapor and the downflowing liquid inside an industrial fractionating column. Such trays are shown in Figures 4 and 5.
The efficiency of a tray or plate is typically lower than that of a theoretical 100% efficient equilibrium stage A theoretical plate in many separation processes is a hypothetical zone or stage in which two phases, such as the liquid and vapor phases of a substance, establish an equilibrium with each other. Such equilibrium stages may also be referred to as a ...
. Hence, a fractionating column almost always needs more actual, physical plates than the required number of theoretical vapor–liquid equilibrium
In thermodynamics and chemical engineering, the vapor–liquid equilibrium (VLE) describes the distribution of a chemical species between the vapor phase and a liquid phase.
The concentration of a vapor in contact with its liquid, especially a ...
stages.
 In industrial uses, sometimes a packing material is used in the column instead of trays, especially when low pressure drops across the column are required, as when operating under
In industrial uses, sometimes a packing material is used in the column instead of trays, especially when low pressure drops across the column are required, as when operating under vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often dis ...
. This packing material can either be random dumped packing ( wide) such as Raschig ring
Raschig rings are pieces of tube, approximately equal in length and diameter, used in large numbers as a packed bed within columns for distillations and other chemical engineering processes. They are usually ceramic, metal or glass and provide a la ...
s or structured sheet metal. Liquids tend to wet the surface of the packing, and the vapors pass across this wetted surface, where mass transfer
Mass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location (usually meaning stream, phase, fraction or component) to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration ...
takes place. Differently shaped packings have different surface areas and void space between packings. Both of these factors affect packing performance.
See also
*Azeotropic distillation
In chemistry, azeotropic distillation is any of a range of techniques used to break an azeotrope in distillation. In chemical engineering, ''azeotropic distillation'' usually refers to the specific technique of adding another component to gener ...
*Batch distillation Batch distillation refers to the use of distillation in batches, meaning that a mixture is distilled to separate it into its component fractions before the distillation still is again charged with more mixture and the process is repeated. This is in ...
*Continuous distillation
Continuous distillation, a form of distillation, is an ongoing separation in which a mixture is continuously (without interruption) fed into the process and separated fractions are removed continuously as output streams. Distillation is the sep ...
*Extractive distillation
Extractive distillation is defined as distillation in the presence of a miscible, high-boiling, relatively non-volatile component, the solvent, that forms no azeotrope with the other components in the mixture. The method is used for mixtures h ...
*Laboratory glassware
Laboratory glassware refers to a variety of equipment used in scientific work, and traditionally made of glass. Glass can be blown, bent, cut, molded, and formed into many sizes and shapes, and is therefore common in chemistry, biology, and anal ...
* Steam distillation
*Theoretical plate A theoretical plate in many separation processes is a hypothetical zone or stage in which two phases, such as the liquid and vapor phases of a substance, establish an equilibrium with each other. Such equilibrium stages may also be referred to as a ...
*Vacuum distillation
Vacuum distillation is distillation performed under reduced pressure, which allows the purification of compounds not readily distilled at ambient pressures or simply to save time or energy. This technique separates compounds based on differences i ...
* Fractional distillation
References
External links
Use of distillation columns in Oil & Gas
by Ivar J. Halvorsen and Sigurd Skogestad, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
by Ming Tham, Newcastle University, UK
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140713020048/http://www.distillationgroup.com/distill.htm , date=2014-07-13 by the Distillation Group, USA
Distillation simulation software
Distillation Chemical equipment Fractionation fr:Distillation fractionnée it:Colonna di distillazione